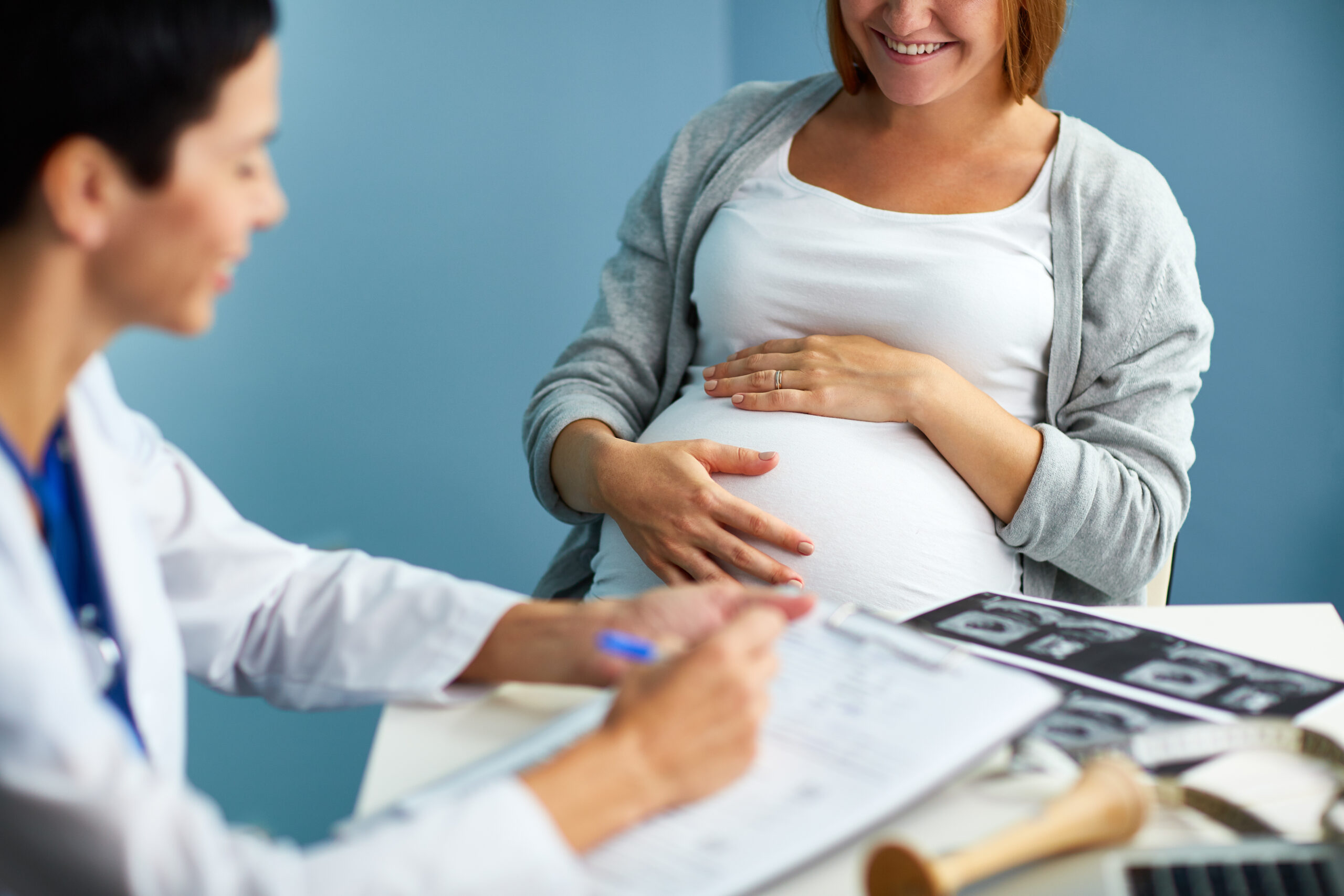
Does complicated pregnancy always lead to cesarean in expecting mothers?
Pregnancy is a unique journey for every woman. While some pass it smoothly, others face complications due to various medical complications. An article in The Hindu reported a study that analyzed data from nearly 24,000 pregnant women in India, finding that the prevalence of high-risk pregnancies is significantly high at 49.4%.
Lets explore here some of the complications that may arise during pregnancy.
-
Preeclampsia: A condition characterized by high blood pressure during pregnancy, which can lead to serious complications for both mother and baby.
-

Gestational Diabetes: A type of diabetes that develops during pregnancy, causing high blood sugar levels.
-

Placenta Previa: A condition where the placenta covers the cervix, which can cause severe bleeding during delivery.
-

Fetal Distress: A situation where the baby shows signs of stress, often indicated by an abnormal heart rate.
-

Multiple Pregnancies: Pregnancies involving more than one baby, such as twins or triplets, which may also increase the risk of complications.
-

Abnormal Fetal Positions: When the baby is positioned in a way that makes vaginal delivery difficult or unsafe, such as being breech (feet or buttocks first) or transverse (sideways).
The severity and type of complications greatly determines if a c-section is the only solution. The perspective and treatment given by the healthcare professionals also plays a vital role in the delivery of the baby.
Factors influencing the decision for a cesarean in mothers

-

Maternal Health: Conditions like high blood pressure, heart disease, or other chronic illnesses may sometimes pose a threat to the mother or/and the baby. Under such circumstances, when normal delivery seems like a threat to their wellbeing, c-section often became the safer option.
-

Fetal Health: Fetal distress, abnormal heart rate, or developmental concerns can result in a decision for a caesarean in mothers. The goal is to minimize stress on the baby and prevent complications that could arise from a prolonged or difficult labor.
-

Obstetric History: Previous C-sections, uterine surgeries, or complicated deliveries can influence the mode of delivery in subsequent pregnancies. A history of uterine rupture or significant scarring may make a vaginal delivery risky.
Alternatives and Considerations

-

Vaginal Delivery: Despite complications, some pregnancies can be managed with careful monitoring, allowing for a vaginal delivery. This decision depends on the nature of the complication and the overall health of the mother and baby.
-

Medical Interventions: Healthcare team uses techniques such as induction of labor, use of forceps, or vacuum-assisted delivery before opting for a C-section. These interventions can sometimes facilitate a vaginal birth even in complicated pregnancies.
-

Risks and Benefits: Both vaginal and cesarean deliveries come with risks and benefits. Vaginal delivery typically has a shorter recovery time and lower risk of infection, while a C- section may be safer in certain high-risk scenarios. Each case must be evaluated individually to determine the best course of action.
Case-by-Case Basis

-

Personalized Care: The decision for a C-section is often made on a case-by-case basis, considering the unique factors of each pregnancy. Healthcare providers assess the risks and benefits for the mother and baby, aiming to choose the safest delivery method.
-

Consultation with Specialists: High-risk pregnancies may require consultation with maternal-fetal medicine specialists. These experts help determine the best delivery method, taking into account all medical factors and potential complications.
Statistics and Trends for a C-section

There has been a global increase in C-section rates, partly due to better detection and management of complications. Factors like improved prenatal care and monitoring technologies also contribute to this trend, allowing for timely interventions when necessary.
Organizations like the World Health Organization (WHO) provide guidelines on when C-sections are medically necessary. These guidelines help ensure that C-sections are performed only when absolutely required, avoiding unnecessary surgeries.
Conclusion
It's very important and necessary for expectant mothers to be informed about the different options available and the potential outcomes of them. Informed consent ensures that mothers understand the risks and benefits associated with both vaginal and cesarean deliveries and became a part of the decision-making process. Consulting with healthcare professionals and understanding the risks and benefits can help expectant mothers make informed decisions about their delivery options.
While many complicated pregnancies do result in C-sections, it is not a universal outcome. It is rather based on the severity and safest method of delivery that plays a pivotal role. Advances in medical research and technology has helped better management of complicated pregnancies. These advancements may reduce the need for C-sections in some cases, offering safer alternatives for both mother and baby.




